Configuring print queues
Introduction
When Watchdoc is installed, a default configuration is defined for the (one or more) print queues detected by Watchdoc. This configuration can be changed at any time. Furthermore, it is possible to add other print queues to the existing queues.
This section explains how to configure and manage your print queues.
What is a print queue?
The print queue is a holding place where the print-job is placed before it is sent to the print device (dedicated printer or multifunction device).
When the devices are installed on a network, the print queue is common to all of the workstations and therefore contains all of the print jobs sent by all of the network users.
A print queue is assigned to a single device, but it is possible to declare a number of queues for a single device, especially if the device handles black and white and colour printing.
The queue groups all of the print orders that the printer has to execute in order to print one or more jobs.
Configuration principle
To place a device under the control of Watchdoc, it is essential to configure the print queue assigned to it in Watchdoc.
For every device declared, a shared print queue is generated by default. Until it is configured, the print queue is operational but not controlled by Watchdoc.
Configuring a print queue is the same as assigning a shadow queue to the shared queue generated by default.
In most configurations, Watchdoc corresponds to a printing device.
Organisational requirements
Before proceeding to configure a print queue in Watchdoc, check that there is at least one device declared on the print server and that its driver is installed and that the shared queue exists.
Role of the print queues
-
Shared queue: A queue generated by default by the print wizard when the network printing device is installed. This queue is not controlled by Watchdoc. Its function is to generate the spool
 Waiting queue before sending to the peripheral. The word 'spool' originally stands for 'simultaneous processing operations on line'.
The print spool is the output file sent to the printing device. It contains all the commands the printer needs to execute in order to print one or more documents. corresponding to the print jobs sent to the device.
Waiting queue before sending to the peripheral. The word 'spool' originally stands for 'simultaneous processing operations on line'.
The print spool is the output file sent to the printing device. It contains all the commands the printer needs to execute in order to print one or more documents. corresponding to the print jobs sent to the device. -
Shadow queue: A queue created by Watchdoc when the shared queue is configured. This queue hosts the print spool controlled by Watchdoc and its function is to send it to the print device after analysis.
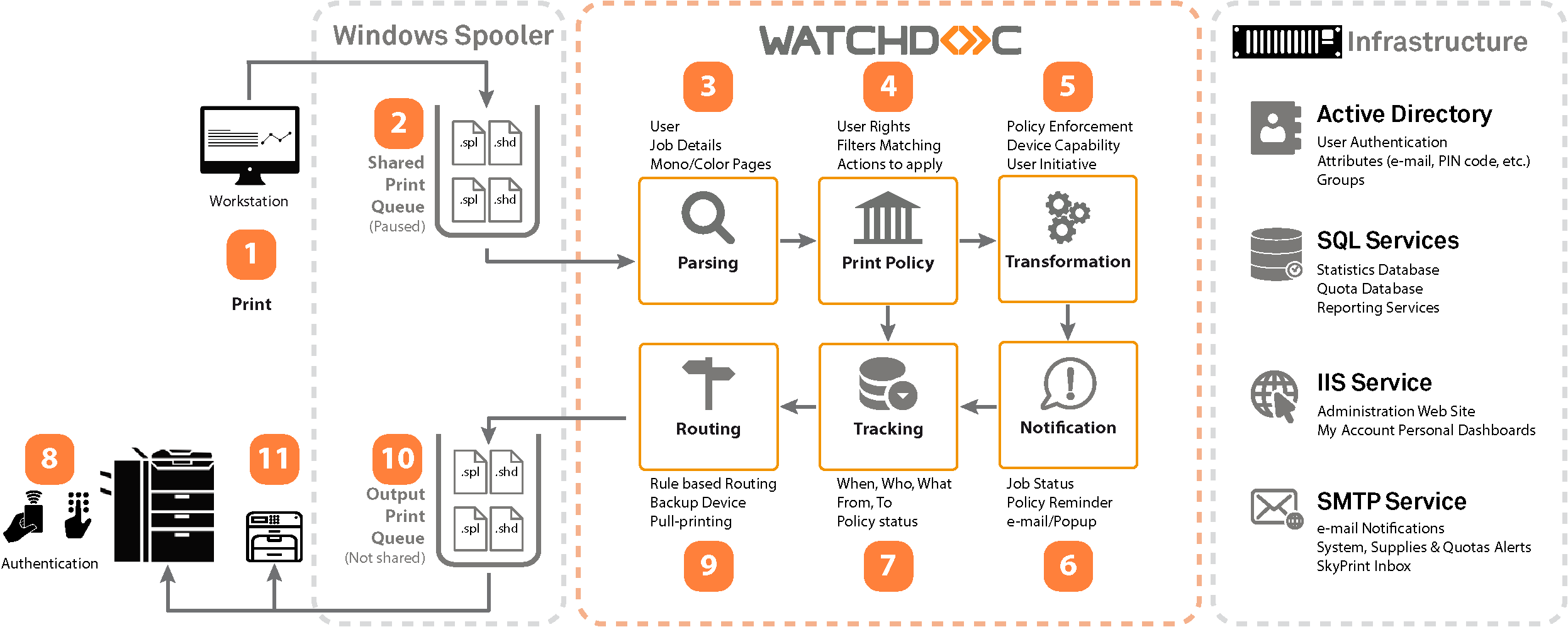
For every print job present in the shared queue, Watchdoc:
-
analyses the two files (.spl and .shd) generated by the spooler,
-
extracts the data that is subject to the filters (in line with the printing policy),
-
extracts the authentication data that it subjects to the LDAP directory (to check that the user can be found there).
-
If no filter blocks the printing and the user is recognised in the directory, Watchdoc moves the spools that have been analysed to the shadow queue which then sends them to the device for printing.